The Challenge of Low User Adoption in Health Tech
The adoption of health technologies has the potential to revolutionise healthcare delivery, improving patient outcomes and operational efficiency. However, low user adoption remains a persistent barrier, preventing these solutions from achieving their full impact. Without widespread implementation and integration, digital health solutions cannot effectively scale, limiting their ability to enhance patient care and system efficiency.
Barriers to Health Tech Adoption
Several challenges hinder the uptake of health tech solutions. A study examining digital health technology adoption found that while these innovations can streamline workflows and reduce workload pressures for healthcare workers, adoption is often slowed by:
- Technological anxiety and resistance to change.
- Concerns over return on investment for healthcare organisations.
- Organisational and environmental barriers, such as leadership commitment, regulatory constraints, and infrastructure limitations.
- User distrust, particularly among older adults, due to concerns over data privacy and lack of digital literacy.
- Disparities in access, especially in low-resource settings, contribute to inequitable adoption rates.

Source: Reaching the commercialization summit, Jan Bordon, Chuck Gammal, Alexandre Habib, Kay Schultze
Strategies to Drive Adoption
To address these challenges and drive adoption, stakeholders must focus on several key areas:
1. Improving Usability and Training
Health tech solutions should prioritise user-friendly designs that align with existing clinical workflows. Comprehensive training programs for healthcare workers can reduce technological anxiety and promote seamless integration.
2. Engaging Stakeholders Early
Involving end-users from the outset of the design and implementation process increases buy-in and ensures solutions meet real-world needs. Programs like the Digital Health Translation and Implementation Program (DHTI) in Australia highlight the importance of infrastructure support and stakeholder collaboration.
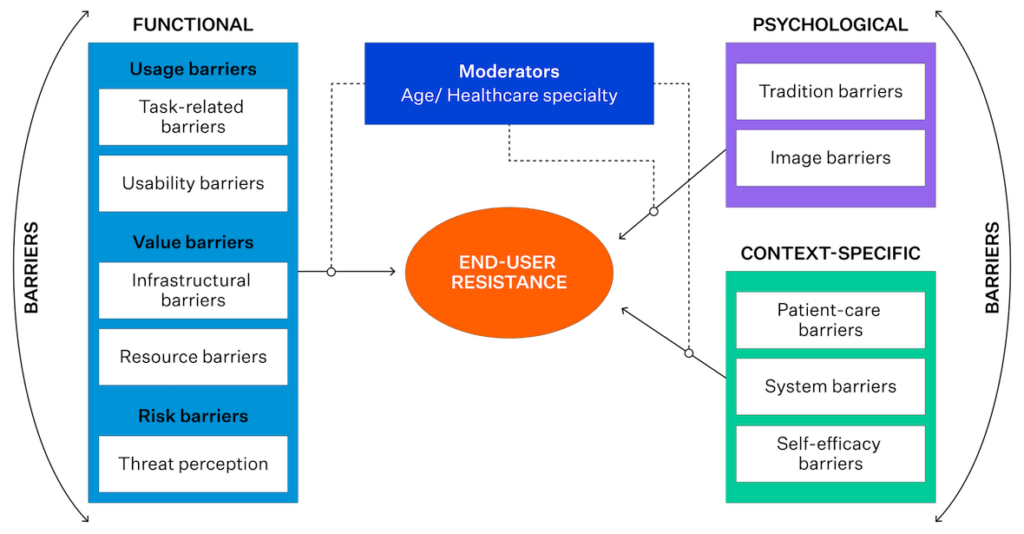
Source: Iyanna, S., Kaur, P., Ractham, P., Talwar, S., & Islam, A. N. (2022). Digital transformation of healthcare sector. What is impeding adoption and continued usage of technology-driven innovations by end-users?. Journal of Business Research, 153, 150-161
3. Building Digital Trust
Transparent data governance, robust privacy protections, and digital literacy initiatives targeted at vulnerable populations are essential to address digital distrust. Trust-building measures encourage greater confidence in digital health technologies.
4. Developing Sustainable Business Models
Digital health companies must prioritise scalable business models that:
- Demonstrate clinical value.
- Navigate regulatory complexities.
- Attract investment.
- Leverage government-backed incentives, such as professional development funding and technology adoption grants, to accelerate uptake.
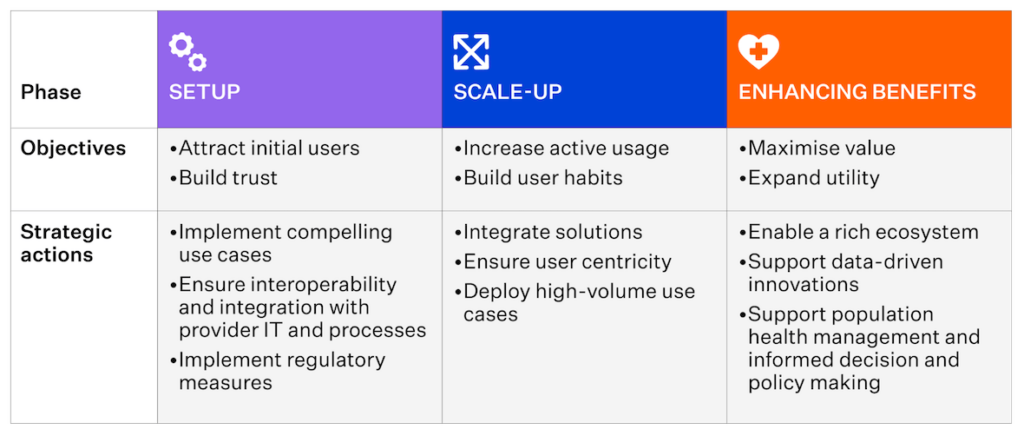
Source: Scaling national e-health: Best practices from around the world, McKinsey
Ensuring the Success of Digital Health Solutions
The success of digital health solutions hinges on overcoming adoption barriers through strategic engagement, training, and trust-building measures. By addressing these challenges, health tech can be more effectively scaled, ensuring its transformative potential is fully realised for both patients and healthcare systems.
—–
Ready to drive the adoption of digital health solutions in your organisation? Discover how Orion Health’s innovative technologies and expert support can help you navigate adoption challenges and scale effectively. Get in touch with the team.




